Difference between revisions of "Building brewing water with dissolved chalk"
(→Calculating the salt additions) |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
= Calculating the salt additions= | = Calculating the salt additions= | ||
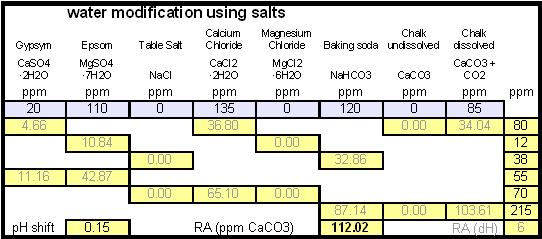
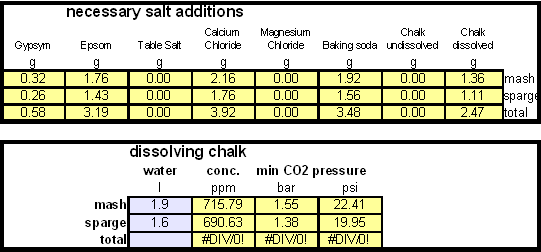
| + | In order to calculate the addition of dissolved chalk correctlt you need a brewing water spreadsheet that supports dissolved chalk. Most of the available spreadsheets don't since they assume that each chalk molecule contributes only one bicarbonate ion. My water spread sheer, [http://braukaiser.com/documents/Kaiser_water_calculator.xls Kaiser_water_calculator.xls] supports both dissolved and undissolved chalk in brewing water. In general, when dissolving chalk only half the amount of chalk is needed to build waters with the same residual alkalinity. | ||
| + | ==Step 1== | ||
| + | |||
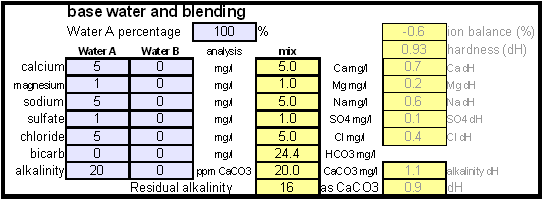
| + | Enter the starting water profile. I use reverse osmosis water which is very soft water and for which I have a water analysis. If you are using reverse osmosis water and don't have an analysis simply leave the fields for the starting water profile 0. Due to the low ion concentration compared to the final ion concentration of the brewing water the error will be minimal and too small to matter. | ||
[[Image:Dissolving_chalk_base_water.gif|center]] | [[Image:Dissolving_chalk_base_water.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Step 2== | ||
[[Image:Dissolving_chalk_salts.gif|center]] | [[Image:Dissolving_chalk_salts.gif|center]] | ||
Revision as of 01:02, 10 December 2009
|
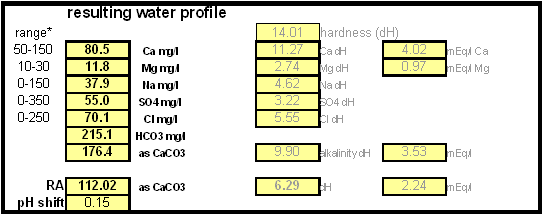
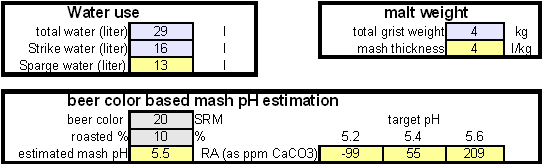
In order to be able to build brewing water with a profile that matches a particular city or to build any brewing water that has temporary hardness chalk (CaCO3) is needed. Chalk, however, is not very soluble in water and most of what needs to be added remains suspended or settles to the bottom. The acidic environment of a mash will eventually dissolve that chalk but not as complete as one would think. Experiments with dissolved and undissolved chalk have shown that the alkalinity potential of undissolved chalk is limited. In particular it was only able to raise the mash pH by up to 0.2 pH units regardless how much was added. Dissolved chalk, on the other hand, did not show these limitations. While chalk can be dissolved in water using acids, it defeats the purpose since the use of acids counteracts the alkalinity that the chalk is supposed to give the water. Only when chalk is dissolved by using CO2 is it able to raise the alkalinity of the water. The addition of CO2 creates carbonic acids which is able to convert the chalks carbonate ion (CO32-) to a bicarbonate ion (HCO3-). While doing that the carbonic acids itself is converted to bicarbonate. In the end one dissolved molecule of chalk (CaCO3) contributes 2 bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) and 1 calcium (Ca2+) ion to the water. To brew an upcoming batch of Kaiser Alt I want to mimic the water profile of the city of Düsseldorf where most of the Alts are brewed in Germany. One of the most well known Alt breweries there, Zum Uereige, does not use city water. According to this on-line statement the brewing water for that brewery comes from their own deep well. The Düsseldorf public water however is essentially cleaned and treated water from the river Rhein. The current water report for Düsseldorf is available on-line: Water report Düsseldorf and upon calculating the residual alkalinity for that water one finds 108 ppm as CaCO3 or 6.1 dH (dH is German Hardness). Such a residual alkalinity is well suited for brewing a dark amber beer like an Alt and I assume that most Alt breweries use city water without any water treatment. Calculating the salt additionsIn order to calculate the addition of dissolved chalk correctlt you need a brewing water spreadsheet that supports dissolved chalk. Most of the available spreadsheets don't since they assume that each chalk molecule contributes only one bicarbonate ion. My water spread sheer, Kaiser_water_calculator.xls supports both dissolved and undissolved chalk in brewing water. In general, when dissolving chalk only half the amount of chalk is needed to build waters with the same residual alkalinity. Step 1Enter the starting water profile. I use reverse osmosis water which is very soft water and for which I have a water analysis. If you are using reverse osmosis water and don't have an analysis simply leave the fields for the starting water profile 0. Due to the low ion concentration compared to the final ion concentration of the brewing water the error will be minimal and too small to matter. Step 2
|